Intent Class
A data structure that represents
- An operation to be performed
- An event that has occurred
Intent as desired operations
Intents provide a flexible language for specifying operations to be performed.
Intent is constructed by one component that wants some work done
Received by one activity that can perform that works
Intent Fiels
Action
- action_dial - dial a number
- action_edit - display data to edit
- action_sync - synchronize device data with server
- action_main - start as initial activity of app
Data
- Data associated with the intent
- Formatted as a URI (uniform resource identifier)
Category
- Additional information about the components that can handle the intent
Type
- Specifies the MIME type of the intent data
Component
- The component that should receive this intent
- Use this when there's exactly one component that should receive the intent
Extras
- Add'l information associated with intent
- treated as a map
Flags
- Specify how intent should be handled
The target activity
Can be named explicitly by setting the intent's component
Can be determined implicitly
Implicit activation
When the activity to be activated is not explicitly named, Android tries to find activities that match the intent
This process is called intent resolution process
- An intent describing a desired operation
- IntentFilters which describe which operations an activity can handle
-- Specified either in AndroidManifest.xml or programmatically
Intent Resolution Data
Action
Data (Both URI & TYPE)
Category
Priority
Android:Priority - Priority given to the parent component when handling matching intents
Causes Android to prefer one activity over another
Value should be greater than 1000 & less than 1000
Hiver values represent higher priority
Permissions
Android protects resources & data with permissions
Used to limit access to:
- User information
- cost-sensitive API's
- System resources
Permissions are represented as strings
In AndroidManifest.xml, apps declare permissions
They require of other components
Using Permissions
Apps specify permissions they use througha <uses-permission> tag
Users must accept these permissions before an application can be installed
Defining Permissions
Suppose your application performs a privileged/dangerous operation
You might not want to allow just any application to invoke yours
So you can define & enforce your own permission
Component Permissions
Individual components can set their own permissions, restricting which other components can access them
Component permissions take precedence over application-level permissions
Activity permissions
restricts which components can start the associated activity
Checked within execution of
- startActivity()
- startActivityForResult()
Throws SecutityException on permissions failure
onCreateView() must return the View at the root of the Fragments's layout
This view is added to the containing activity
Fragment Class
Represents a behavior / portion of UI within an activity
Multiple fragments can be embedded in an activity to create a Multi-pane UI
A single fragment can be reused across multiple activities
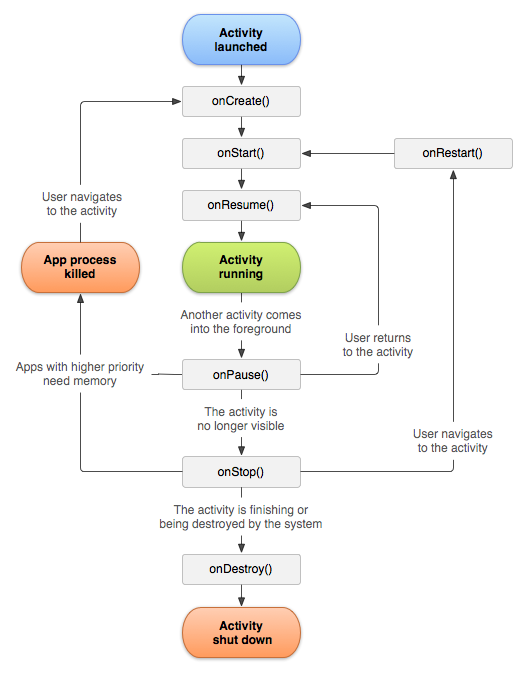
Fragment lifecycle is coordinated with the lifecycle of its containing activity
Fragments have their own lifecycles and receive their own callbaks
Adding Fragments to Activities
Two general ways to add fragments to an activity's layout
- Declare it statically in the activity's layout file
- Add it programmatically using the FragmentManager
Layout can be inflated/implemented in onCreateView()
Adding Fragments Dynamically (Frame layout)
While an activity's running you can add a fragment to it's layout
- Get reference to the FragmentManager
- Begin a FragmentTransaction
- Add the fragment
- Commit the FragmentTransaction
Dynamic Layout
Fragment transactions allow you to dynamically change your app's user interface
Can make the interface more fluid & take better advantage of available screen space
Configuration Changes
If you call setRetainInstance(true), Android won't destroy the Fragment on configuration changes
Results in some changes to lifecycle callback sequence
onDestroy() will not be called
onCreate() will not be called
Questions
Which of the following statements describe common uses of the Intent class?
To specify an operation to be performed.
To represent an event that has occurred.
If you want to send a message to a particular person using an Intent with the Intent.ACTION_SENDTO action, what one other piece of Intent information do you have to set?
See: http://developer.android.com/reference/android/content/Intent.html#ACTION_SENDTO for more information.
Data.
Which one of the following flags will help you get more information about how Android determines which Activities can respond to a given Intent?
Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_LOG_RESOLUTION.
Which of the following Intent fields are used as match criteria during Intent resolution?
Category.
Action.
Data
Which of the following describe situations where permissions might be used?
To restrict access to costly operations.
To restrict accesps to device hardware features.
To restrict access to user data.
Which XML tag does an application use to specify permissions that the device's user must grant to the application before that application can run on the user's device.
<uses-permission>
Which XML tag or attribute is used to specify an application-specific permission that an application may require of any other application that wants to interact with it?
<permission>
Which Exception is thrown if one Activity tries to start another Activity for which it does not have the appropriate permissions?
SecurityException.
When designing an application's user interface, it's a good practice to design a single, identical user interface for both Tablets and Phones.
False
Which one of the following Fragment lifecycle callback methods occurs at the earliest point in the Fragment lifecycle?
onAttach().
In which method does a Fragment normally create its user interface?
onCreateView().
When an application programatically adds a Fragment to an Activity, it normally performs the four steps shown below. Which of these steps is done last?
Commit the FragmentTransaction
When a Fragment is programmatically added to an Activity, by default Android adds the new Fragment to the Task backstack.
False
Which one of the following Fragment methods tells Android not to destroy a Fragment when a device configuration change occurs?
setRetainInstance().
Suppose that an application includes an Activity named A, and that the application declares an <activity> tag for A within its AndroidManifest.xml file. If Activity A should be the main entry point for this application, then it will specify an <intent-filter> element, containing an <action> element. What value should you include to complete the following <action> element definition - <action android:name= "…."/>?
android.intent.action.MAIN
Suppose that an application includes an Activity named A and that the application declares an activity tag for A within its AndroidManifest.xml file. If Activity A will be the main entry point for its application and if an icon for this application/activity should appear in the top-level launcher, how should you complete the following <category> element - <category android:name="…"/>?
android.intent.category.LAUNCHER
The MapLocationFromContacts application created an Intent with the Action, Intent.ACTION_PICK and a with data URI representing the contacts database. It then invoked an Activity using startActivityForResult(). What type of data will the started Activity return?
A String Uri.
Suppose you create an application that uses the Vibration Service to make a device vibrate as a deadline approaches. To receive permission to use the Vibrator Service, you will need to add a <uses-permission> element to your application's AndroidManifest.xml file. What permission value should you use to complete the <uses-permission> element - <uses-permission android:name="…"/>?
See: http://developer.android.com/reference/android/Manifest.permission.html for more information.
android.permission.VIBRATE
Suppose you create an application that captures and stores personal information from the user, such as the medicines they are currently taking. Other applications may want to use this information and then provide add-on services over it, for example, to create 'time to take your pill' reminders. Which of the following tags would you put in your application's AndroidManifest.xml file to define a new application-specific permission for accessing your application.
<permission>.
The Fragment class is a subclass of the Activity class and replaces Activities on large screen devices such as Tablets.
False
In which method do Fragments typically create their user interfaces?
onCreateView().
Which of the following are good reasons for dynamically modifying application layouts at runtime, rather than by using static layout files.
Dynamic layouts can take advantage of contextual information that's not tracked by Android's configuration system (such as current location, usage time, or ambient light measurements).
Dynamically-created user interfaces can adapt to an application's runtime state, such as the amount of data that needs to be displayed at any one time.
Suppose you have an Activity that hosts a Fragment. This Fragment has invoked the setRetainInstance() method, passing in the parameter true. Which of the following Fragment lifecycle methods will not be called if the Activity is later killed and restarted due to a reconfiguration?
onDestroy().
onCreate().
Enjoy
Marcos Carvalho












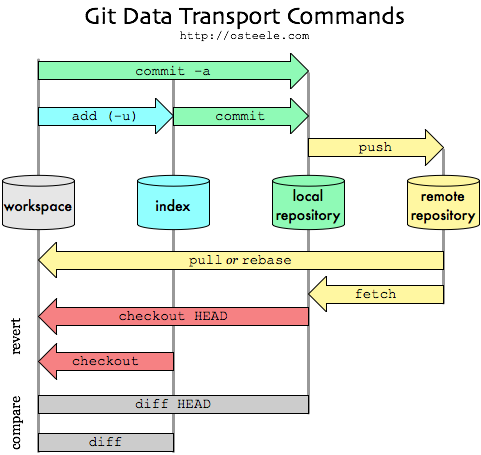
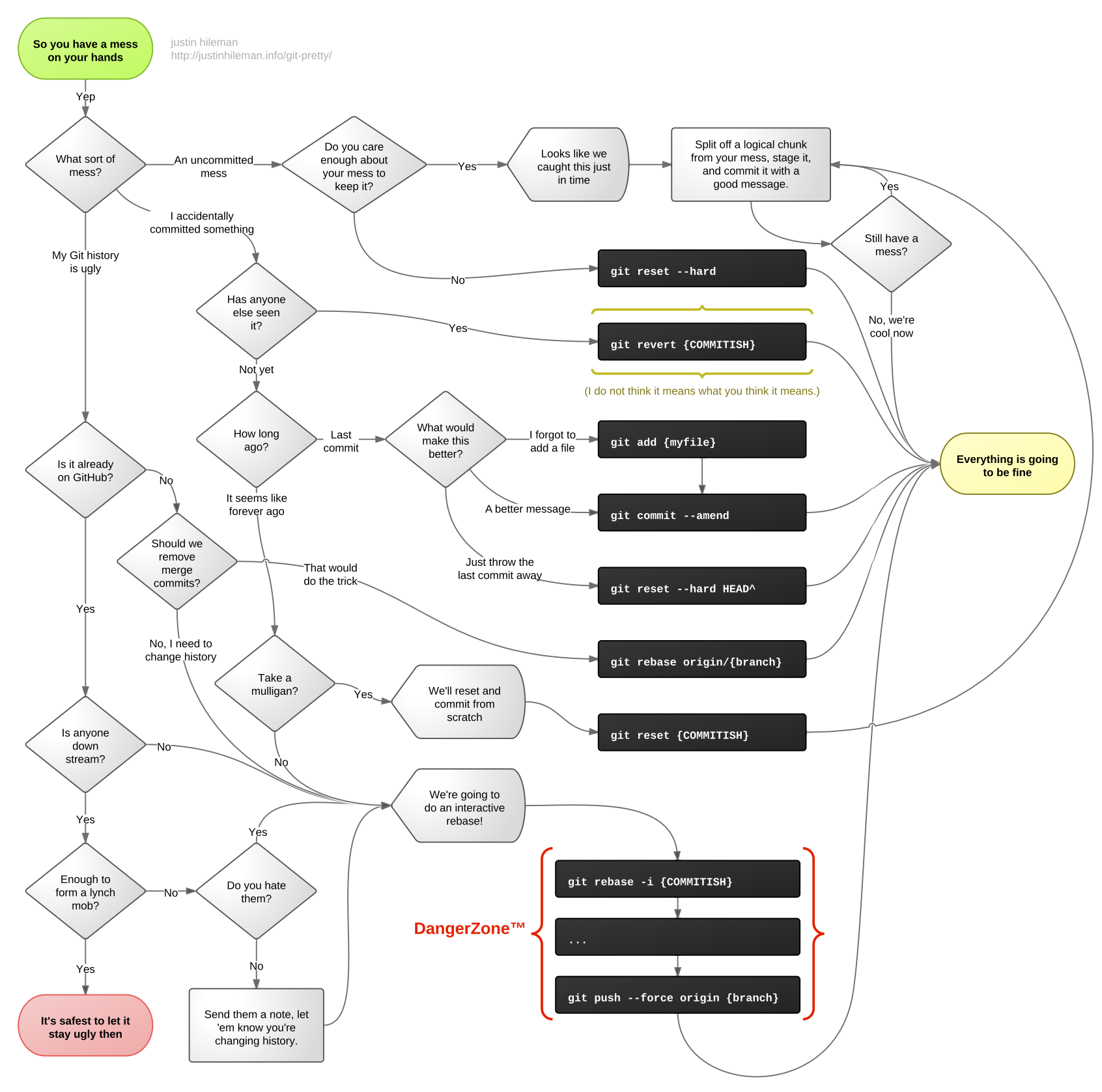
 Estou adicionando esse post porque através do Git, consegue-se elevar o nível de trabalho e cuidado com o código.
Estou adicionando esse post porque através do Git, consegue-se elevar o nível de trabalho e cuidado com o código.